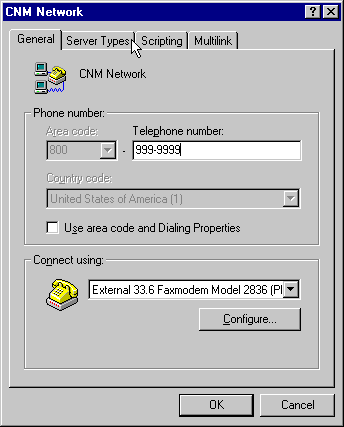
NOTE: A common mistake is to put your own phone number in this field, instead of the number for the CNM Network Dial-Up. Make sure this is not the case.
NOTE: The text for this check-box is different depending on your version of Dial-Up Networking. Windows 98 (Dial-Up Networking 1.3) has the "Use area code..." text. Most versions of Windows 95 will say "Use country code...".
NOTE: This could cause a dialing error if checked. If you hear an operator's voice when dialing your modem, this may be the problem. Also, this setting is often the cause of "not answering" errors or busy signals.
NOTE: Problems finding the modem are usually caused by this setting. The entries you find in this field come from the list of drivers installed on your system. Sometimes, we find that there is more than one driver for a particular modem installed on the system. Usually the different drivers reference different communication (Com) ports. If dial-up networking cannot locate the modem, check to see if there are other drivers installed here. If there is more than reference to the modem you are using, often the last in the list is the current one.
NOTE: Whether you have the tab or button depends on the version of Dial-Up Networking you have installed on your computer.
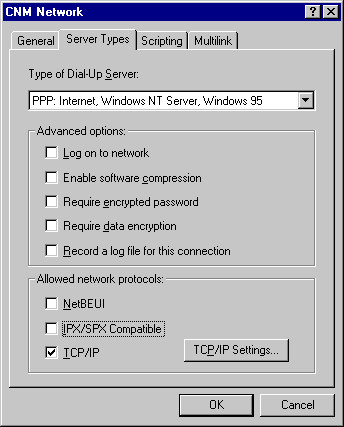
NOTE: The default windows settings for the "Advanced Options" is "Log on to network" checked, and "Enable software compression" checked. This should be changed for use with CNM Network.
"Log on to network" causes the connection to attempt to sign on to a Microsoft network. This setting can cause problems during authentication.
"Enable software compression" causes the connection to attempt to use the PPP Compression Control Protocol (CCP), which many internet providers (CNM included) does not support. This can cause many errors during authentication, and is also the cause of many user's problems with being disconnected while online. CCP works independently of modem compression.
NOTE: The default windows settings for the "Allowed network protocols" is to have all options checked. If NetBEUI or IPX/SPX Compatible are checked, uncheck them.

NOTE: We do not generally specify name server addresses in case these IP addresses change. This has not been an issue for CNM in the past, but as we are aware of some ISPs which do specify name server addresses and have needed to change their name server addresses, but did not notify their customers about this change. This created a great number of problems for users trying to open internet sites.
NOTE: Sometimes, it is helpful to specify the name server addresses if you are having trouble reaching to sites once online. For information on how to do this, click here.
